Bottom Line Up Front: As consumers have increasingly integrated smart technology into their households, the influx of smart gadgets brings understandable privacy concerns, especially since many of these companies have a controversial history of recording and reviewing users’ voice data without their consent. So, while the latest exploit termed a Near-Ultrasound Inaudible Trojan is targeted towards smart assistants and mobile devices, it is in fact not a new attack vector and was first noticed circa 2015. While I could not audibly hear your angst, I have always got my antennae up when I walk in the valley of the shadow of the Digital Exhaust Ecosystem. I am going to provide you with several ways to protect your privacy and reduce your vulnerabilities to this attack vector which is exploiting the smart assistant and mobile devices as a threat vector.
Cross-Device Tracking Overview
Cross-device tracking is a method used by companies to track the online behavior of users across multiple devices, such as smartphones, tablets, and computers. It allows companies to collect data on how users interact with websites, apps, and other online services on multiple devices, in order to build a more complete picture of the user’s behavior and preferences.
Cross Device Tracking Using Ultrasonic Inaudible Sound Beacons
Cross-device tracking using ultrasonic inaudible sound beacons, also known as “ultrasonic tracking”, is a technique that involves emitting high-frequency audio signals from one device, such as a television or a smartphone, which are then picked up by the microphones on other nearby devices, such as laptops, tablets, or other smartphones.
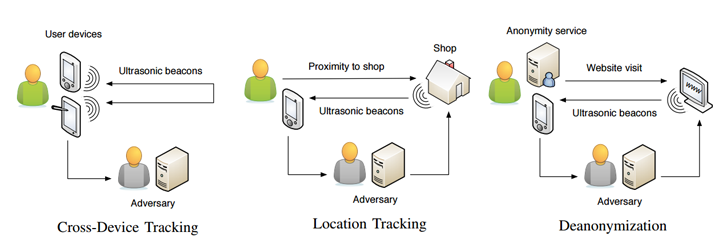
The ultrasonic signals are typically embedded in audio or video content, such as TV commercials or online ads. When a user is exposed to this content on one device, their other nearby devices that have microphones can pick up the signal and send a message back to the advertising company, identifying the user and linking their behavior across devices. (EDITOR’S NOTE: For further information about previous examples of how ultrasonic tracking has been used previously in both advertising and attack vectors, please navigate to the following link.)
The Federal Trade Commission evaluated ultrasonic tracking technology at the end of 2015, and the privacy-focused non-profit Center for Democracy and Technology wrote to the agency at the time that “the best solution is increased transparency and a robust and meaningful opt-out system. If cross-device tracking companies cannot give users these types of notice and control, they should not engage in cross-device tracking.”
The advantage of using ultrasonic signals is that they are inaudible to humans, so users are not aware that their devices are communicating with each other. This makes it both a stealthy and effective way to both track and attack users across multiple devices. (EDITOR’S NOTE: For further information about how ultrasonic tracking can be used to de-anonymize TOR users, please navigate to the following link.)
Near-Ultrasound Inaudible Trojan (NUIT) Overview
For background, the Near-Ultrasound Inaudible Trojan (NUIT) is a novel inaudible attack against voice assistants (Siri, Google Assistant, Alexa, Cortana) that can be executed remotely through internet.
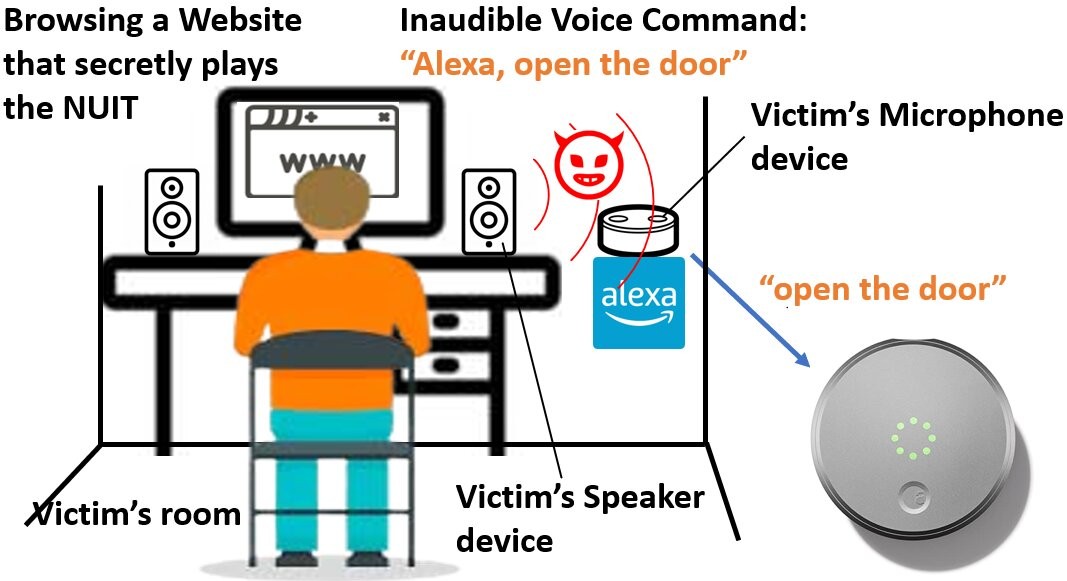
NUIT appears as a sound clip in near-ultrasound frequency range (16kHz-20kHz), thus can be played on the target’s speaker to attack the voice assistant or a target’s other devices. (EDITOR’S NOTE: The following link will demonstrate how this works in real time.)
Countermeasures To NUIT Attacks Via Smart Assistants
To disable microphone access in the Alexa app, here are steps you can take to adjust key settings:
- Open the Alexa app on your smartphone or tablet.
- Tap the menu icon (three horizontal lines) in the top left corner of the screen
- Select “Settings.”
- Tap on “Alexa Account” at the top of the page.
- Scroll down and select “Recognized Voices.”
- Toggle off the switch next to “Voice Profiles.”
(EDITOR’S NOTE: This will prevent Alexa from recognizing your voice and responding to your commands.)
To disable voice commands in Siri, here are steps you can take to adjust key settings:
- Open the “Settings” app on your iPhone or iPad.
- Select “Siri & Search.”
- Toggle off the switch next to “Listen for ‘Hey Siri.'”
(EDITOR’S NOTE: This will prevent Siri from automatically listening for your voice commands and responding to them. If you want even more information about ways Siri can eavesdrop, check out my 27 October 2022 Smoke Signal.)
To disable voice commands in Google Assistant, here are steps you can take to adjust key settings:
- Open the Google Assistant app on your smartphone or tablet.
- Tap on your profile picture in the top right corner of the screen.
- Select “Assistant settings.”
- Scroll down and select “Assistant.”
- Toggle off the switch next to “Hey Google.”
(EDITOR’S NOTE: This will prevent Google Assistant from automatically listening for your voice commands and responding to them. If you want even more information about ways, you can configure your privacy to prevent Smart Assistants from eavesdropping, check out my 29 December 2021 Smoke Signal.)
Countermeasures To NUIT Attacks Via PCs And Macs
To disable microphone access in Cortana on a Windows 10 PC, here are steps you can take to adjust key settings:
- Click on the Start menu and open Settings.
- Click on Privacy.
- Click on Speech, inking, & typing in the left-hand menu.
- Under the “Speech” section, click on the “Turn off speech services and typing suggestions” button to disable Cortana.
Alternatively, you can leave speech services turned on and disable Cortana’s access to your microphone specifically by following these steps:
- Click on the Start menu and open Cortana
- Click on the Settings icon (the gear icon) in the left-hand menu.
- Under the “Hey Cortana” section, toggle off the switch next to “Respond when you say, ‘Hey Cortana.'”
(EDITOR’S NOTE: This will prevent Cortana from automatically listening for your voice commands and using your microphone. However, keep in mind that other apps or features on your PC may still have access to your microphone, so you may want to disable microphone access for those as well if you want to ensure complete privacy.)
The steps to disable microphone access on a PC or laptop may vary depending on the operating system you are using but these prompts should get you close for Windows:
- Click on the Start menu and open Settings.
- Click on Privacy.
- Click on Microphone in the left-hand menu.
- Toggle off the switch next to “Allow apps to access your microphone.”
To disable microphone access on macOS, here are steps you can take to adjust key settings:
- Click on the Apple menu and open System Preferences.
- Click on Security & Privacy.
- Click on the Privacy tab.
- Click on Microphone in the left-hand menu.
- Uncheck the box next to any apps that you do not want to have access to your microphone.
Conclusion
The Good Book says in Ecclesiastes that “whatever has happened that is what will happen again; whatever has occurred that is what will occur again. There is nothing new under the sun.” While I may not be as wise as King Solomon, I have seen a few nasty tricks in my years around the Sun so while this attack vector is not new, the threat vector certainly is with the proliferation and adoption of smart assistants and voice command accessibility on our collective mobile devices.
