General Rule is to explore your settings. App settings, device settings, and changes to settings that happen often with updates. You don’t have to be a tech, to get the general understanding that your information is being tracked and sold, and you’re not even being paid royalties. Here’s some more iPhone Opt-Out Settings for this holiday Easter.
Bottom Line Up Front: Most people simply buy an iPhone and start using it out of the box, but it is worth slowing down as there are some nasty privacy Easter Eggs that are hiding in plain sight. The iPhone System Services, which includes various features such as location-based suggestions, cell network search, and network & wireless features, can have severe privacy implications for users. The collection and processing of personal data by these features can lead to the exposure of sensitive information, including a user’s location, internet activity, and contacts and only feeds the Digital Exhaust Ecosytsem when left enabled.
iPhone Cell Network Search Overview
Cell Network Search is a location-based service that sends your location information, and the tower IDs of the network towers within range of (and thus detected by) a user’s phone. It is used by Apple marketing (and whomever they choose to sell/share the database with) to decide patterns of cell usage, tower congestion and so on.
This exchange of information can include the phone’s unique identifier, location data, and other identifying information can be used to track the user’s movements.When you turn on your iPhone, it searches for available cellular networks in the area and connects to the one with the strongest signal.
How Does The iPhone Cell Network Search Work?
The iPhone cell network search process works as follows:
- The iPhone sends a signal to nearby cell towers, asking for available networks.
- The cell towers respond with the available networks in the area.
- The iPhone analyzes the available networks based on factors such as signal strength, network type (2G, 3G, 4G, or 5G), and carrier preferences set by the user.
- The iPhone then selects the network with the strongest signal and sets up a connection.
- If the preferred carrier is not available, the iPhone will connect to another available carrier based on the user’s carrier settings.
The iPhone cell network search happens automatically in the background, and the user does not have to manually search for networks. However, the user can choose to manually select a network from the available options in the iPhone’s settings.
As the iPhone cell network search is an automated process allowing the phone to connect to the nearest cell tower or available cellular network. When a user turns on their iPhone or moves to a new location, the device searches for the nearest available cell tower or network to set up a connection. This process occurs in the background, and the user is not prompted or needed to take any action.
(EDITOR’S NOTE: Those features in System Services are all about sending your location-based information TO Apple, not about enabling features or services on your iPhone. This is Apple’s way of allowing you to opt out of the collection of location-based data that previously was done surreptitiously without overtly letting you know or have any way to stop it.)
iPhone Location-Based Suggestions Overview
The iPhone’s location-based suggestions feature uses a combination of GPS, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth technologies to figure out a user’s location and offer relevant suggestions.
How Does The iPhone Location-Based Suggestions Work?
When a user enables location services on their iPhone, the device periodically sends a request to Apple’s servers, which then responds with a list of nearby Wi-Fi hot spots and cell towers. The iPhone then uses this information to calculate its location.
In addition to Wi-Fi and GPS, the iPhone also uses Bluetooth to decide a user’s location. Bluetooth beacons emit a unique signal that can be picked up by nearby devices, including the iPhone. By detecting the signal strength of these beacons, the iPhone can figure out a user’s approximate location and offer relevant location-based suggestions.
While the iPhone’s location-based suggestions can provide users with a range of useful information and suggestions, such as nearby restaurants, stores, and attractions it can come at a serious cost of a user’s privacy as it requires the device to track a user’s location to supply relevant suggestions.
(EDITOR’S NOTE: Users who are concerned about their privacy can disable location services or limit the use of this feature in their device settings.)
iPhone Location-Based Alerts Overview
The iPhone’s location-based alerts use the phone’s GPS and other location services to provide users with relevant information based on their current location. This feature enables users to receive location-specific notifications and reminders for things like calendar events, reminders, and even local weather updates.
When enabled, the location-based alerts feature uses the phone’s location services to figure out the user’s current location. This can be done through GPS, Wi-Fi, and cellular network data. Once the user’s location has been found, the iPhone checks for any location-based alerts or notifications that have been set up for that specific area.
How Does The iPhone Location-Based Alerts Work?
For example, if a user has set a reminder to pick up groceries when they are near a specific grocery store, the iPhone’s location-based alerts will send a notification to the user when they are in the vicinity of that store. Similarly, if a user has set up a location-based reminder to call a friend when they are in a certain city, the iPhone will send a notification to remind the user when they arrive in that location.
To protect user privacy, the iPhone allows users to control which apps can access their location data. Users can also choose to turn off location services altogether or only allow location access while using certain apps. Additionally, users can view which apps have recently accessed their location data and disable location access for specific apps if desired.
It is worth noting that while location-based alerts can be convenient and helpful, they also pose potential privacy risks. If a user allows certain apps to access their location data, those apps can potentially track the user’s movements and activities.
(EDITOR’S NOTE: It is important for users to be mindful of which apps they allow to access their location data and to regularly review their location access settings to ensure their privacy is protected as these setting are on by default when a user sets up an iPhone.)
iPhone Networking & Wireless Feature Overview
The iPhone uses several technologies to connect to the internet and other devices wirelessly as detailed below:
- Wi-Fi is one of the most used wireless technologies on the iPhone.
Bluetooth allows users to connect to other Bluetooth-enabled devices, such as speakers, headphones, and smartwatches. - Cellular data is another networking feature on the iPhone. The iPhone automatically switches between Wi-Fi and cellular data depending on which network is stronger and faster in each location.
- AirDrop is another networking feature on the iPhone that allows users to share files, photos, and other media wirelessly with other Apple devices.
- AirDrop uses Wi-Fi and Bluetooth to transfer files securely and quickly between devices.
(EDITOR’S NOTE: To protect their privacy when using Networking & Wireless features on their iPhone, it is recommended users should take few key steps to include using a virtual private network (VPN) to encrypt their data when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks; disabling Bluetooth when it is not needed, and carefully reviewing the privacy policies of any apps or services that require access to their location or other sensitive data.)
Disabling These Features In iPhone System Services
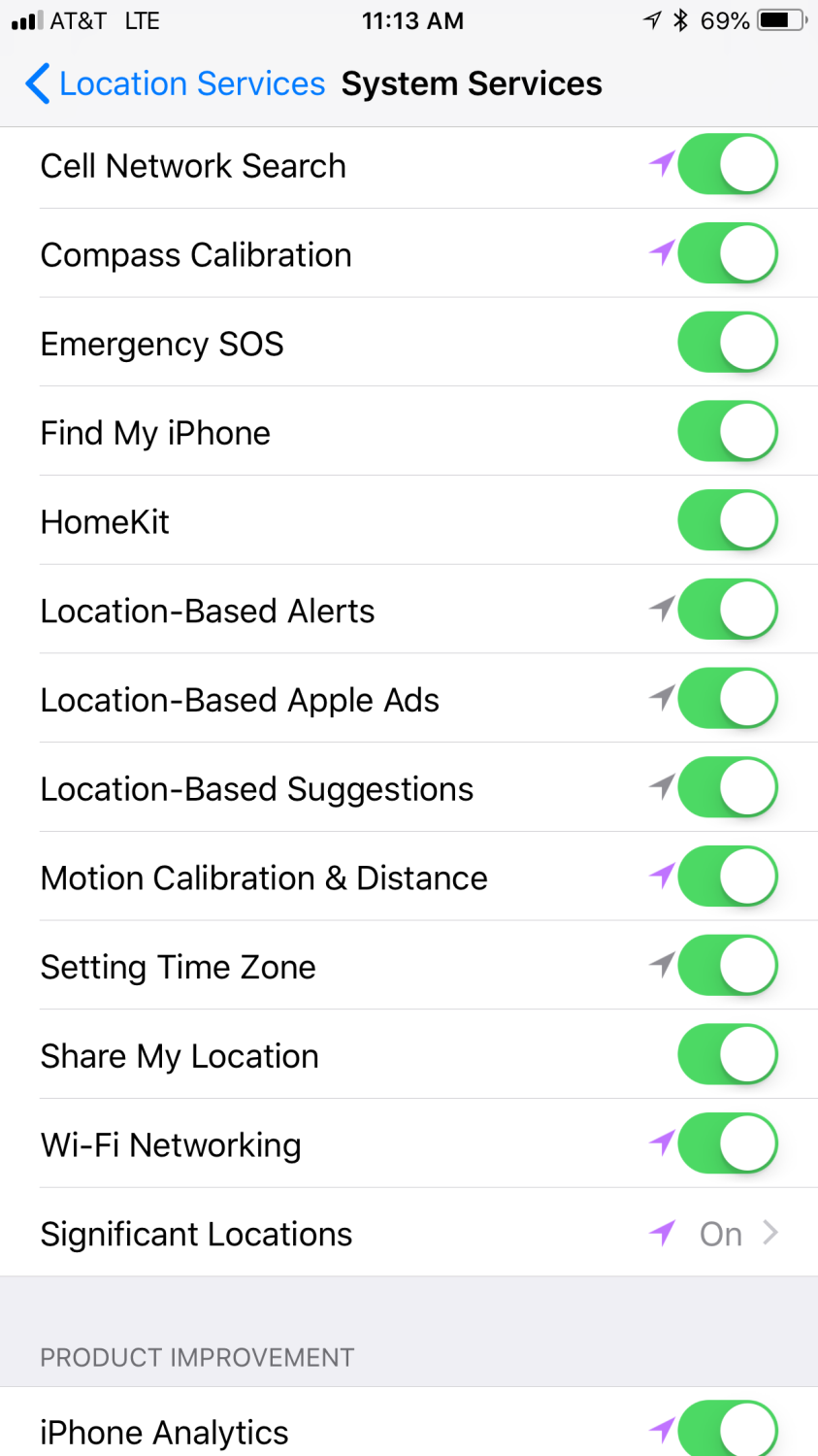
After reading what I have provided, you can navigate to these settings and should you choose to disable these features in iPhone System Services, follow these steps:
- Open the Settings app on your iPhone.
- Scroll down and tap on “Privacy”.
- Tap on “Location Services”.
- Scroll all the way down and tap on “System Services”.
- Here, you will find a list of these key features.
- To disable a feature, simply toggle the switch next to it to the off position.
Conclusion
In the spirit of Easter, I figured I would just tell you where the Easter Eggs were when it comes to preserving your privacy and combating the Digital Exhaust Ecosystem. The collection and processing of personal data by these features can lead to the exposure of sensitive information, including a user’s location, internet activity, and contacts.
One major concern is the potential misuse of user data by third-party apps or services that may have access to the iPhone System Services. Another potential privacy risk is the sharing of user data with Apple. While the company has stated that it collects location data anonymously and uses it to improve its services, some users may be uncomfortable with their personal data being collected and stored by a large corporation.
To mitigate these privacy risks, users can take steps such as disabling the iPhone System Services or restricting the access of third-party apps to their personal data. It is also important to stay informed about the privacy policies of apps and services that are used on the device and to read the terms and conditions carefully before granting access to personal data.
Overall, while the iPhone System Services can offer useful features for users, it is important to be aware of the potential privacy implications and take steps to protect personal data.
